In modern agriculture, accuracy matters more than ever. GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) antennas are playing a vital role in enabling real-time precision for farmers and agricultural equipment manufacturers.
From autonomous tractors to drone-assisted field surveys, GNSS RTK antennas ensure centimeter-level accuracy—improving yield, reducing waste, and increasing operational efficiency.
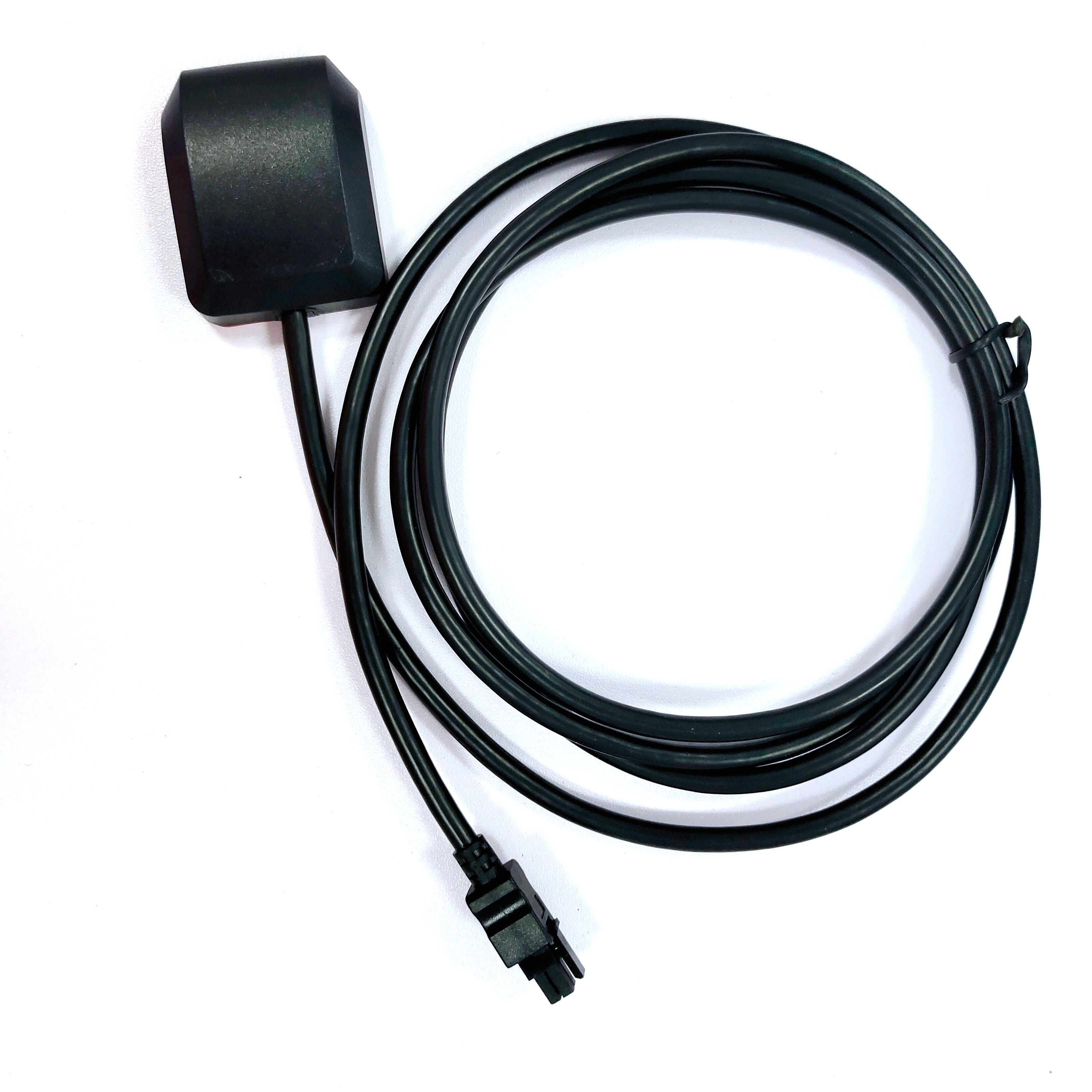
At TOXU, we design and manufacture high-performance GNSS antennas tailored for rugged farming environments. Our mushroom-style RTK antennas support multi-system (GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, BeiDou) and dual-frequency (L1/L2/L5) reception, making them ideal for base stations, auto-steering systems, and precision mapping.
✅ Rugged waterproof design
✅ RTK-ready with low noise amplifiers
✅ Custom connectors and cable lengths
✅ Proven in-field performance with leading OEMs
Want to learn how our GNSS antennas can optimize your agri-tech solutions? Reach out to us anytime — we're here to support innovation in the field.
What is a GPS Ceramic Antenna?
A GPS ceramic antenna is a passive component designed to receive navigation signals from Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) constellations. Built with a ceramic substrate tuned to a specific frequency, such as 1575.42 MHz, it offers high stability, strong anti-interference performance, and compact size—making it ideal for embedded solutions in automotive, UAV, IoT, and surveying devices.
What Does “Satellite Acquisition” Mean?
Satellite acquisition refers to the process in which a GPS receiver searches for and locks onto available GNSS satellites after startup. Depending on stored data and signal conditions, acquisition can be classified as:
Cold Start: No prior data; takes the longest
Warm Start: Partial data retained; faster acquisition (10–30 seconds).
Hot Start: Full data retained; lock achieved within seconds.
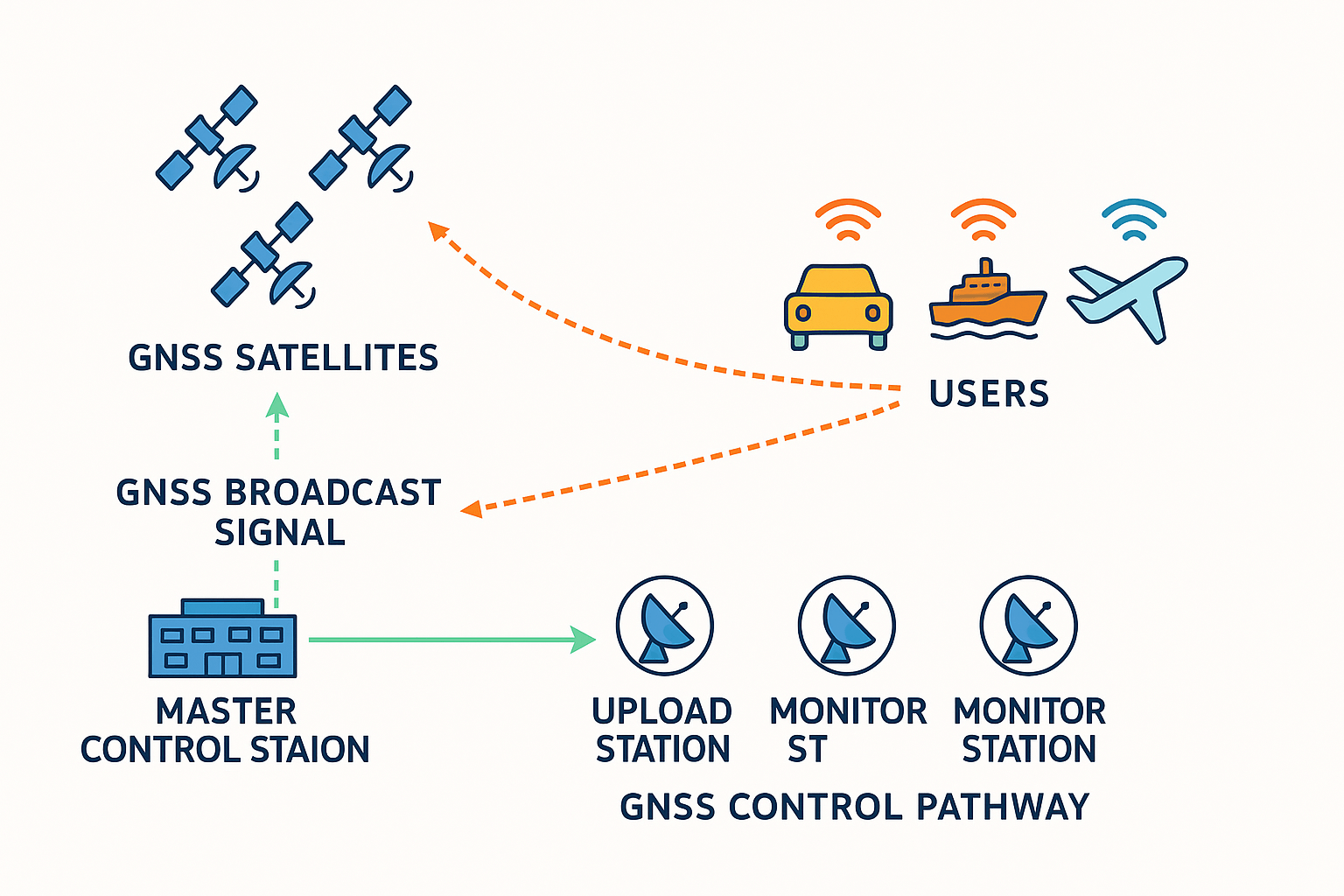
How GPS Ceramic Antennas Acquire Satellites
(See the GNSS Signal Transmission & Control Flow Diagram below)
Signal Reception – The ceramic antenna captures L1 band signals from multiple GNSS satellites.
Signal Amplification & Filtering – Signals pass to the RF front-end (e.g., LNA) for low-noise amplification.
Data Decoding – The receiver extracts navigation messages, including satellite position and time.
Position Calculation – With signals from at least four satellites, the receiver computes 3D position and provides accurate timing.
Factors Affecting Acquisition Speed
Antenna Performance: Higher gain, lower VSWR, and optimized directivity improve acquisition time.
Installation Location: Clear sky view and minimal obstructions boost signal quality.
Satellite Visibility: More visible satellites mean faster positioning.
Environmental Interference: Urban canyons, tunnels, and indoor environments can delay acquisition.
Applications Across Industries
GPS ceramic antennas are widely used in:
Automotive navigation and fleet management
UAV guidance and mapping
Precision surveying and land measurement
Maritime navigation and aviation positioning




































































 Language
Language
 En
En Cn
Cn Korean
Korean

 Home >
Home > 














