To understand the significance of the TOXU Surveying GNSS Antenna, it is essential to first grasp the role of GNSS technology in modern surveying. Traditional surveying methods, reliant on optical instruments and manual measurements, are time-consuming, labor-intensive, and prone to human error. GNSS technology revolutionized the field by leveraging signals from satellites to determine precise geographic coordinates, enabling surveyors to work more efficiently and accurately. At the heart of this technology is the GNSS antenna, which captures satellite signals and transmits them to a receiver for processing. The quality of the antenna directly impacts the accuracy, reliability, and efficiency of the entire surveying operation.
Surveying GNSS antennas differ from consumer-grade antennas in their ability to handle multiple frequencies, minimize interference, and maintain stable signal reception in diverse conditions. Unlike vehicle-mounted antennas, which prioritize durability and mobility, surveying antennas focus on precision, signal integrity, and compatibility with professional surveying equipment. The TOXU Surveying GNSS Antenna is engineered to excel in these areas, making it an indispensable tool for surveyors, engineers, and geospatial professionals.
The antenna’s design reflects a deep understanding of the challenges faced in surveying work. From urban construction sites with tall buildings to remote rural areas with limited satellite visibility, surveyors operate in environments that can disrupt GNSS signals. The TOXU antenna addresses these challenges through a combination of advanced features, including multi-frequency support, low VSWR, and flexible polarization options, ensuring that it can deliver consistent performance in any setting.
The performance of a surveying GNSS antenna is defined by its technical specifications, each of which plays a critical role in ensuring accurate data collection. Let’s examine the key specifications of the TOXU Surveying GNSS Antenna and their implications for surveying applications:
Frequency Range: The antenna operates across three key frequencies: 1575 MHz (GPS L1), 1616 MHz (a frequency used by certain GNSS constellations, including BeiDou), and 2491 MHz (used by systems like Galileo). This multi-frequency support is essential for modern surveying, as it allows the antenna to receive signals from multiple satellite constellations, including GPS, BeiDou, Galileo, and GLONASS (depending on the specific frequencies supported). By leveraging signals from multiple constellations, the antenna reduces reliance on a single system, improving accuracy and reliability, especially in areas where satellite visibility is limited. For example, in urban canyons, where tall buildings block signals from some satellites, the ability to receive signals from other constellations ensures that the surveyor can still obtain accurate measurements.
Gain: With a gain of 5 dBi, the TOXU antenna strikes a balance between signal amplification and noise reduction. Gain in surveying antennas is a delicate consideration: while higher gain can amplify weak signals, it can also introduce noise and increase susceptibility to interference. The 5 dBi gain is optimized for surveying applications, ensuring that the antenna can capture strong, clean signals without compromising accuracy. This is particularly important in precision surveying, where even minor signal distortions can lead to significant measurement errors.
Polarization: The antenna offers both Right-Hand Circular Polarization (RHCP) and linear polarization options. Polarization refers to the orientation of the electric field of the radio wave, and matching the antenna’s polarization to that of the satellite signals is crucial for optimal reception. GNSS satellites transmit signals with circular polarization, making RHCP ideal for capturing these signals. However, linear polarization may be preferred in certain specialized applications, such as short-range surveys or when working with specific types of receivers. The flexibility to choose between RHCP and linear polarization makes the TOXU antenna adaptable to a wide range of surveying scenarios.
VSWR: The Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR) of the TOXU antenna is an impressive 1.5 or lower. VSWR measures how well the antenna is matched to the transmission line (cable) and receiver. A lower VSWR indicates a better match, meaning less signal is reflected back and more is transmitted to the receiver. For surveying applications, where signal integrity is critical, a VSWR of 1.5 ensures minimal signal loss, preserving the accuracy of the data. This is particularly important when working with weak signals, as even small losses can degrade measurement quality.
Input Impedance: The antenna has an input impedance of 50 ohms, a standard in professional GNSS equipment. Impedance matching between the antenna, cable, and receiver is essential for efficient signal transfer. A mismatch can cause signal reflections, leading to loss and distortion. By adhering to the 50-ohm standard, the TOXU antenna ensures compatibility with a wide range of surveying receivers and cables, simplifying integration into existing workflows.
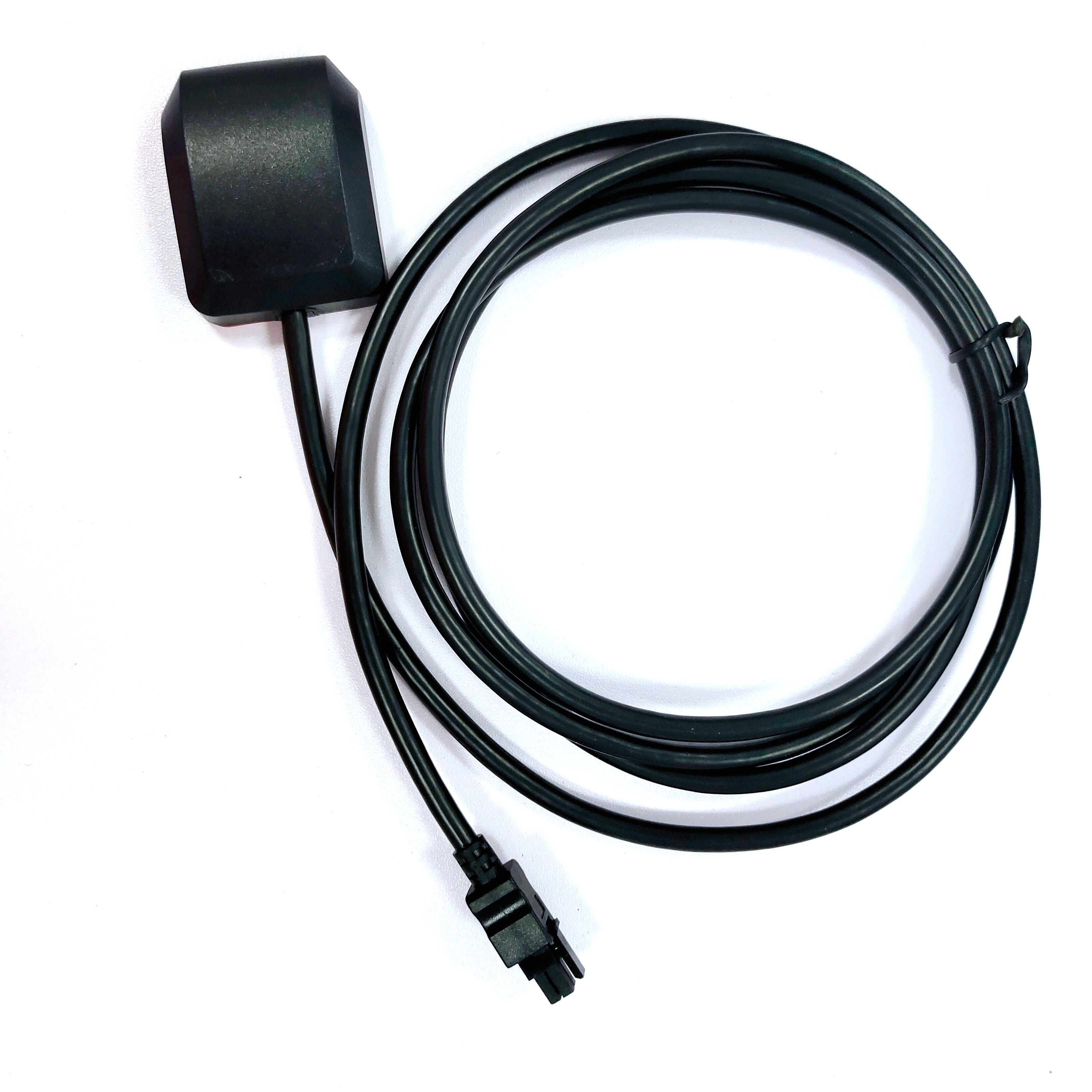
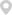
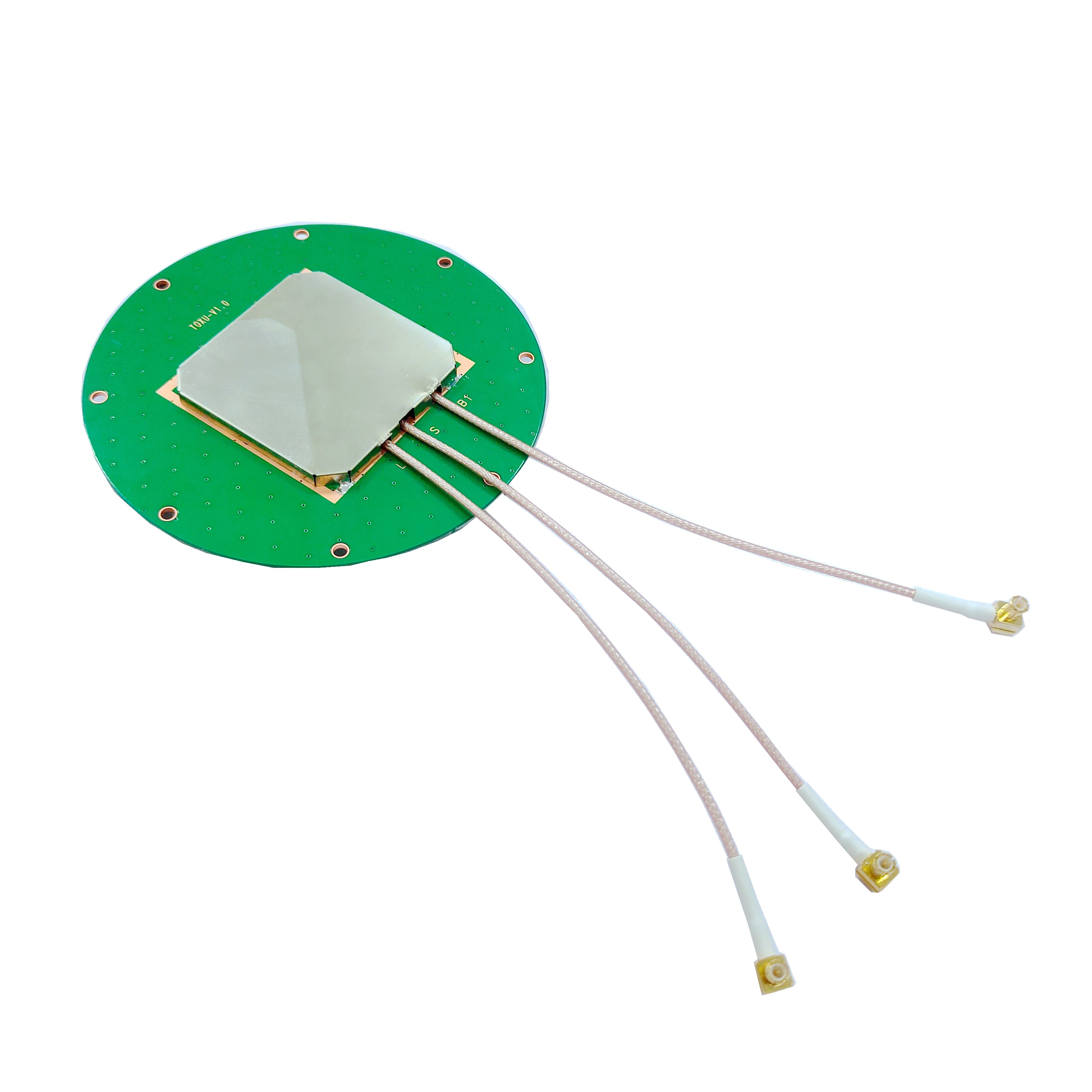
Coaxial Connectors: The TOXU antenna offers a variety of coaxial connectors, including SMA, MCX, MMCX, HRS, and IPX. This versatility is a significant advantage in surveying, where different receivers and equipment may require different connectors. SMA is a common connector in professional GNSS equipment, known for its durability and secure connection. MCX and MMCX are smaller connectors, ideal for applications where space is limited. HRS and IPX connectors are often used in specialized equipment, ensuring that the antenna can be integrated with a wide range of surveying tools. This flexibility eliminates the need for adapters, which can introduce signal loss and complicate setup.
Coaxial Cables: The antenna is compatible with several types of coaxial cables, including RF1.78, RF1.37, RF1.13, and RF0.81. These cables vary in diameter, flexibility, and signal loss characteristics, allowing surveyors to choose the best option for their specific needs. RF1.78 is a larger cable with lower signal loss, ideal for long-distance runs between the antenna and receiver. RF0.81, on the other hand, is a small, flexible cable suitable for situations where maneuverability is important, such as in tight spaces or when using portable equipment. The ability to select the appropriate cable ensures that signal loss is minimized, preserving data accuracy.
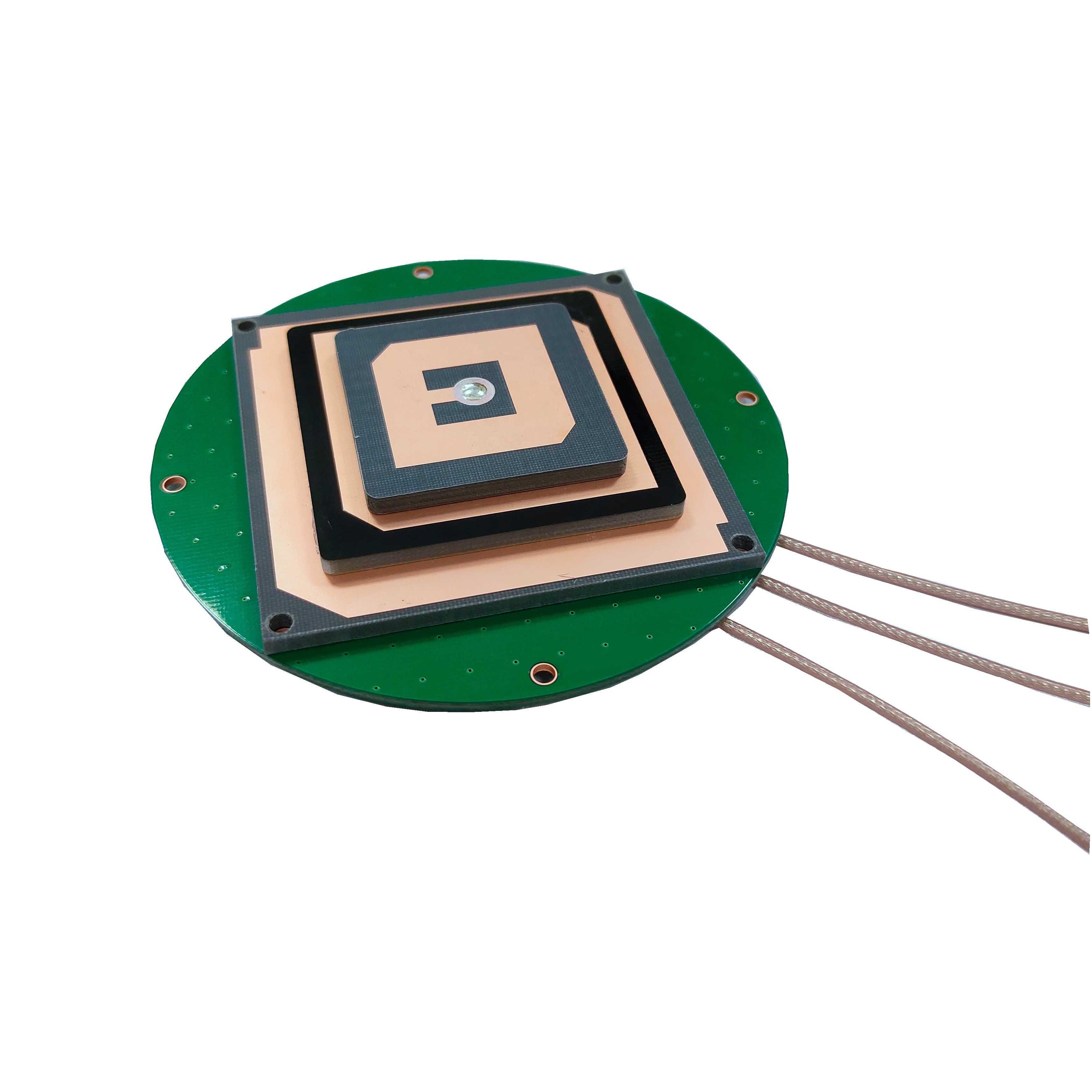
Dimension: The antenna has a compact dimension of 90*13.5 mm, making it highly portable and easy to mount. In surveying, portability is often a key consideration, as equipment must be transported to remote or difficult-to-reach locations. The small size of the TOXU antenna makes it easy to carry and mount on tripods, poles, or other surveying equipment without adding excessive weight or bulk. This compact design also reduces wind resistance, which can cause vibrations and affect measurement stability in outdoor environments.
DC Voltage: The antenna operates on a DC voltage range of 3~5V, which is compatible with most surveying receivers. This low voltage requirement ensures that the antenna can be powered directly by the receiver, eliminating the need for external power sources and simplifying setup. This is particularly valuable in fieldwork, where access to power is often limited.
The TOXU Surveying GNSS Antenna is designed to excel in a wide range of surveying applications, each requiring a high degree of accuracy and reliability. Let’s explore some of the key use cases:
Land Surveying: Land surveying is one of the most common applications for GNSS antennas, involving the measurement and mapping of land boundaries, topography, and features. Accurate land surveys are essential for property transactions, urban planning, and infrastructure development. The TOXU antenna’s multi-frequency support and low VSWR ensure that surveyors can obtain precise coordinates even in challenging terrain, such as hilly areas or dense forests. The compact design and versatile connectors make it easy to integrate with total stations and other land surveying equipment, streamlining the data collection process.
Construction Layout: In construction, precise layout is critical to ensuring that buildings, roads, and other structures are built according to design specifications. The TOXU antenna enables surveyors to mark out foundations, utilities, and structural elements with millimeter-level accuracy, reducing the risk of errors and rework. The antenna’s ability to maintain stable signal reception in construction zones, which are often filled with heavy machinery and obstacles, ensures that layout work can proceed efficiently. The variety of coaxial connectors and cables allows for easy integration with construction-grade receivers, making it a versatile tool on the job site.
Mapping and Cartography: Creating accurate maps and charts requires detailed geospatial data, which is collected using GNSS technology. The TOXU antenna’s multi-frequency support and polarization options make it ideal for mapping applications, whether in urban, rural, or remote areas. For example, in mapping a new road network in a remote region, the antenna’s ability to receive signals from multiple satellite constellations ensures that data can be collected even in areas with limited visibility. The compact design also makes it suitable for use with drones, which are increasingly used in mapping to capture aerial data.
Infrastructure Monitoring: Monitoring the stability of infrastructure such as bridges, dams, and buildings requires precise measurements over time to detect subtle movements that could indicate structural issues. The TOXU antenna’s high accuracy and reliability make it an excellent choice for this application. By collecting consistent data over weeks, months, or years, surveyors can identify trends and alert engineers to potential problems before they become critical. The antenna’s durability and ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions ensure that it can operate continuously in outdoor settings, providing long-term monitoring data.
Mining and Resource Exploration: In mining and resource exploration, accurate surveying is essential for planning extraction operations, mapping mineral deposits, and ensuring safety. The TOXU antenna’s ability to operate in rugged environments, combined with its multi-frequency support, makes it well-suited for these applications. Whether surveying an open-pit mine or exploring a remote mineral deposit, the antenna can deliver precise data, helping companies optimize their operations and reduce costs.
-
Proper installation and integration are critical to maximizing the performance of the TOXU Surveying GNSS Antenna. Surveyors must take care to position the antenna correctly, select the appropriate cables and connectors, and ensure compatibility with their receivers. Here are some key considerations:
Mounting Position: The antenna should be mounted in a location with a clear view of the sky to maximize satellite signal reception. In surveying, this typically means mounting the antenna on a tripod or pole at a sufficient height to avoid obstructions such as trees, buildings, or equipment. The compact size of the TOXU antenna makes it easy to mount on standard surveying tripods, and its low profile reduces the risk of interference from nearby objects. It is also important to ensure that the antenna is level, as an inclined antenna can introduce measurement errors.
Cable Selection: The choice of coaxial cable depends on the specific surveying scenario. For long distances between the antenna and receiver, such as in large construction sites, RF1.78 cable is recommended due to its low signal loss. For shorter distances or when portability is a priority, RF0.81 or RF1.13 cables may be more suitable. It is important to avoid excessive cable length, as longer cables can increase signal loss, especially with smaller diameter cables. Surveyors should also ensure that the cable is routed to avoid sharp bends, which can damage the cable and degrade signal quality.
Connector Compatibility: The TOXU antenna’s variety of connectors ensures compatibility with most surveying receivers, but it is essential to select the correct connector for the specific receiver model. Using the wrong connector or an adapter can introduce signal loss and compromise accuracy. Surveyors should consult their receiver’s documentation to determine the appropriate connector and ensure a secure, tight connection to prevent signal leakage.
Grounding: Proper grounding is important to protect the antenna and receiver from electrostatic discharge (ESD) and lightning strikes, which can damage equipment and corrupt data. In outdoor surveying environments, where the antenna is exposed to the elements, grounding the antenna mount to a suitable earth ground can reduce the risk of damage. Surveyors should follow best practices for grounding, including using copper wire and ensuring a low-resistance connection to the ground.
Calibration: After installation, the antenna should be calibrated to ensure accurate measurements. Calibration involves comparing the antenna’s output with known reference points to correct for any systematic errors. Many surveying receivers include calibration tools that can be used to align the antenna with the receiver’s internal reference frame, ensuring that measurements are consistent and accurate.
Integration with Software: The TOXU antenna works seamlessly with most surveying software packages, which process the GNSS data and generate maps, coordinates, and reports. Surveyors should ensure that their software is compatible with the receiver and antenna, and that the correct antenna model is selected in the software settings to apply appropriate corrections and parameters.
Advantages Over Competing Products
In a market filled with surveying GNSS antennas, the TOXU antenna stands out for several key advantages:
Multi-Frequency Support: By covering 1575 MHz, 1616 MHz, and 2491 MHz, the antenna can receive signals from multiple GNSS constellations, improving accuracy and reliability in diverse environments. This is particularly valuable in regions where certain constellations are more dominant, such as BeiDou in China.
Versatile Connectivity: The range of coaxial connectors (SMA, MCX, MMCX, HRS, IPX) and compatible cables (RF1.78, RF1.37, RF1.13, RF0.81) ensures that the antenna can be integrated with virtually any surveying receiver, eliminating the need for adapters and simplifying setup.
Low VSWR: A VSWR of 1.5 minimizes signal loss, ensuring that the receiver receives strong, clean signals, which is critical for precision surveying. This outperforms many competing antennas with higher VSWR ratings, which can introduce errors in measurements.
Flexible Polarization: The option to choose between RHCP and linear polarization makes the antenna adaptable to different surveying scenarios, ensuring optimal signal reception regardless of the satellite constellation or environment.
Compact and Portable: The 90*13.5 mm dimension makes the antenna easy to transport and mount, which is essential for surveyors working in remote or difficult-to-reach locations. Its lightweight design also reduces fatigue during extended fieldwork.
Cost-Effectiveness: As a product from Guangdong, China, a leading hub for electronics manufacturing, the TOXU antenna offers a competitive price point without compromising on quality. This makes it an attractive option for surveying firms of all sizes, from small businesses to large enterprises.
-
The field of surveying GNSS technology is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in satellite systems, receiver technology, and data processing. The TOXU Surveying GNSS Antenna is well-positioned to adapt to these trends, ensuring that it remains a valuable tool for geospatial professionals in the years to come.
Expanded Frequency Support: As new GNSS constellations and frequencies are introduced, future versions of the TOXU antenna may support additional frequencies, further enhancing accuracy and reliability. For example, the inclusion of Galileo’s E6 frequency or BeiDou’s B3 frequency could provide even more robust signal reception in challenging environments.
Enhanced Anti-Interference Technology: With the increasing use of wireless technologies, GNSS signals are more susceptible to interference from sources such as 5G networks and industrial equipment. Future antennas may incorporate advanced filtering and signal processing techniques to mitigate this interference, ensuring that surveyors can collect accurate data even in noisy electromagnetic environments.
Integration with IoT and Cloud Computing: The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) and cloud computing is transforming surveying workflows, enabling real-time data sharing and remote processing. Future versions of the TOXU antenna may include features that facilitate integration with IoT devices and cloud platforms, allowing surveyors to stream data directly to the cloud for analysis and collaboration.
Miniaturization and Power Efficiency: As surveying equipment becomes more portable, there is a growing demand for smaller, more power-efficient antennas. The TOXU antenna’s compact design already positions it well in this regard, but future iterations may become even smaller while maintaining performance, making them ideal for use with drones and other portable devices.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Optimization: AI algorithms could be used to optimize antenna performance in real-time, adjusting parameters such as gain and polarization to adapt to changing environmental conditions. This would ensure that the antenna always operates at peak efficiency, delivering the most accurate data possible.
Conclusion
The TOXU Surveying GNSS Antenna represents a perfect fusion of precision, versatility, and durability, making it an essential tool for modern geospatial professionals. Its multi-frequency support, low VSWR, flexible connectivity options, and compact design ensure that it can deliver accurate, reliable data in a wide range of surveying applications, from land surveying and construction layout to infrastructure monitoring and resource exploration.
The antenna’s advantages over competing products, including its versatile connectivity, low signal loss, and cost-effectiveness, make it a standout choice for surveying firms looking to enhance their capabilities without breaking the bank. As technology continues to evolve, the TOXU antenna is well-positioned to adapt to new trends, ensuring that it remains at the forefront of surveying GNSS technology.
In a field where accuracy and reliability are paramount, the TOXU Surveying GNSS Antenna provides surveyors with the confidence to tackle even the most challenging projects, delivering results that drive informed decision-making and successful outcomes. Whether working in urban centers, remote wilderness, or rugged construction sites, geospatial professionals can rely on the TOXU antenna to provide the precise data they need to succeed.



































































 Language
Language
 En
En Cn
Cn Korean
Korean

 Home >
Home > 





 18665803017 (Macro)
18665803017 (Macro)













