Applications
Land Surveying: Rugged GNSS survey antennas are used in land surveying for precise mapping, boundary determination, and topographic surveys, enabling accurate data collection in various terrains and weather conditions.
Construction: In construction, these antennas are used for site layout, monitoring, and inspection, ensuring that structures are built according to design specifications and safety standards.
Mining: Mining operations rely on rugged antennas for surveying and mapping underground tunnels, open pits, and waste dumps, improving operational efficiency and safety.
Environmental Monitoring: Environmental agencies use rugged antennas for monitoring changes in land use, vegetation cover, and water levels, providing valuable data for conservation and disaster management efforts.
Future Trends
Miniaturization: Advances in materials science and manufacturing processes will enable the development of even smaller and lighter rugged GNSS survey antennas, expanding their use in portable and wearable surveying devices.
Integration with Other Sensors: The integration of GNSS antennas with other sensors, such as inertial measurement units (IMUs) and cameras, will enhance surveying equipment's situational awareness and data collection capabilities, enabling fully autonomous operations.
Advanced Signal Processing: The development of advanced signal processing techniques, such as software-defined radios (SDRs) and artificial intelligence (AI), will improve the antenna's ability to filter out noise and interference, enhancing positioning accuracy in challenging environments.
Multi-frequency and Multi-constellation Support: Future antennas will support an even wider range of GNSS frequencies and constellations, providing global coverage and improving redundancy and reliability in surveying operations.
Conclusion
Rugged GNSS survey antennas are essential tools that enable surveyors to collect accurate data in challenging outdoor environments. Their robust construction, high performance, and versatility make them ideal for a wide range of applications, from land surveying and construction to mining and environmental monitoring. Despite the challenges associated with their cost, size, weight, and integration, ongoing advancements in materials science, manufacturing processes, and signal processing techniques are driving the evolution of rugged GNSS survey antennas towards even more capable and accessible solutions. As surveying technology continues to advance, rugged antennas will remain at the forefront of innovation, enabling surveyors to navigate the world with unprecedented precision and reliability.



































































 Language
Language
 En
En Cn
Cn Korean
Korean

 Home >
Home > 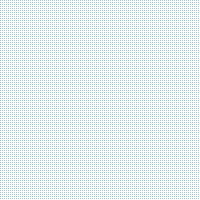





 18665803017 (Macro)
18665803017 (Macro)













