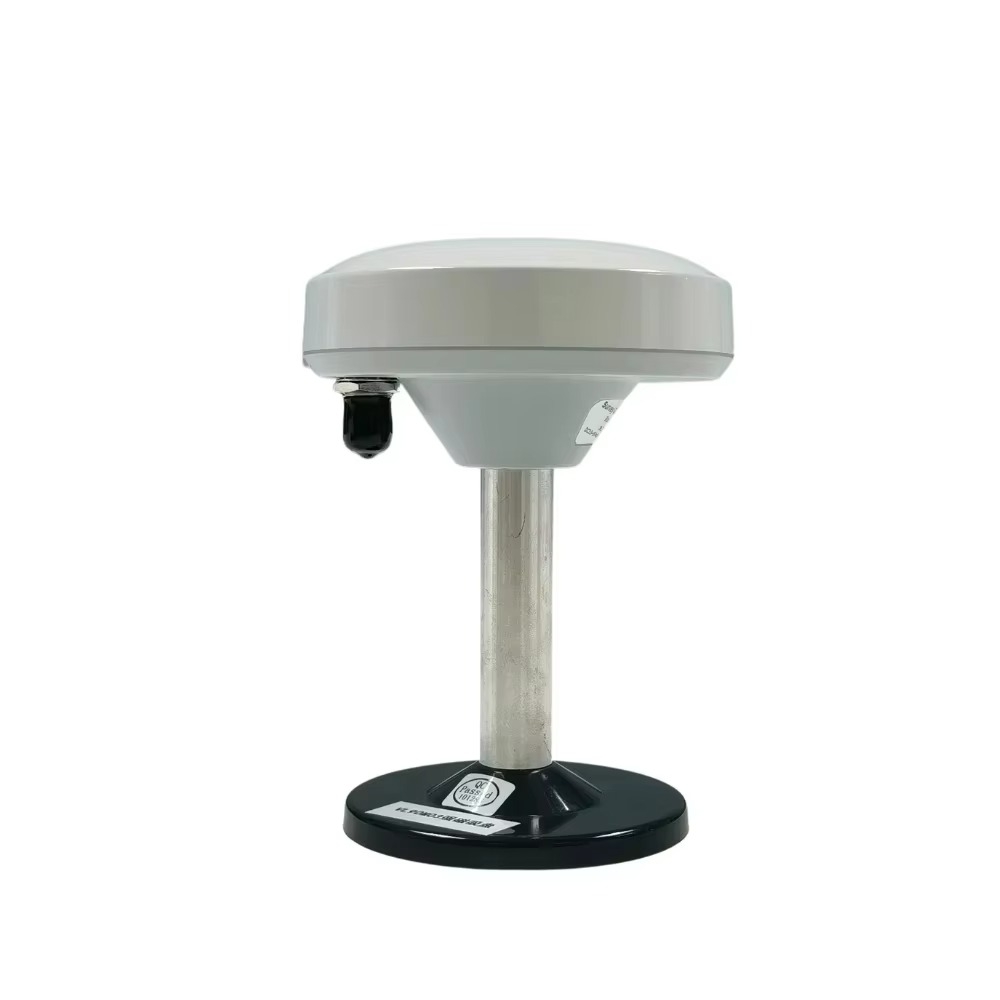
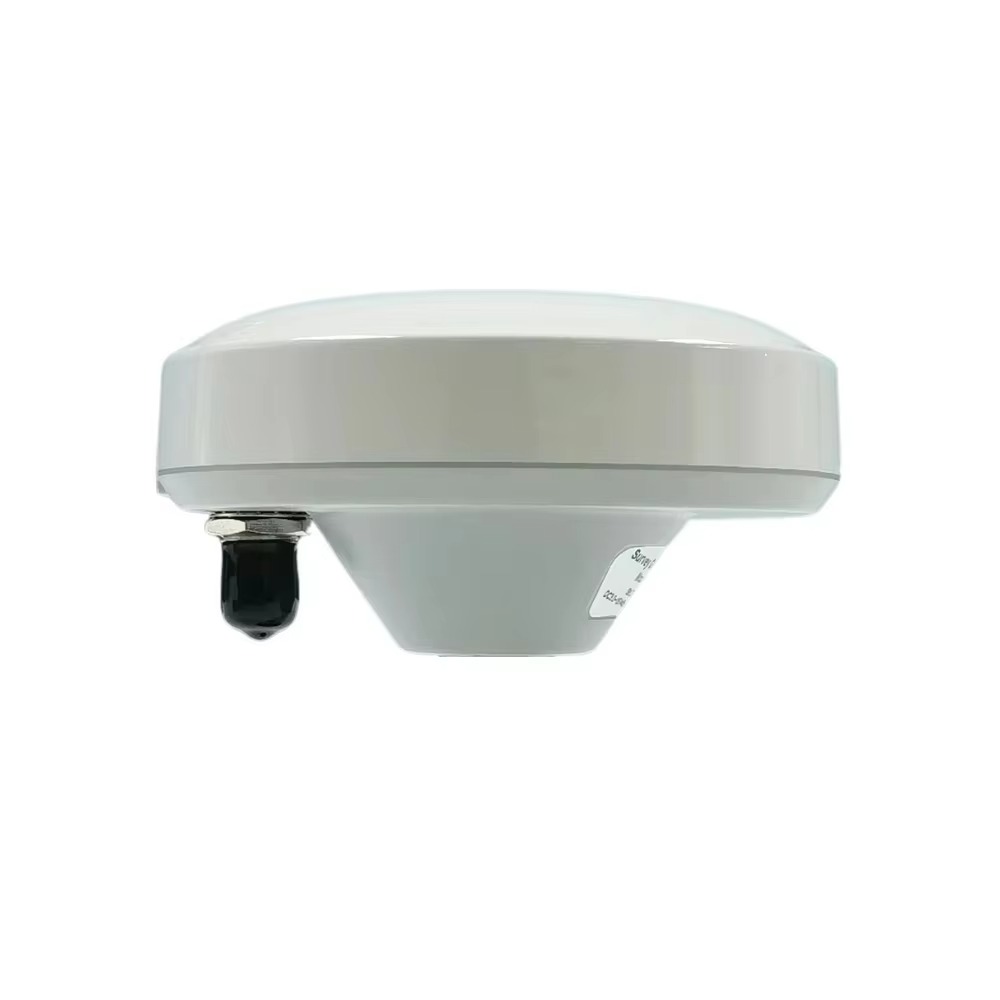
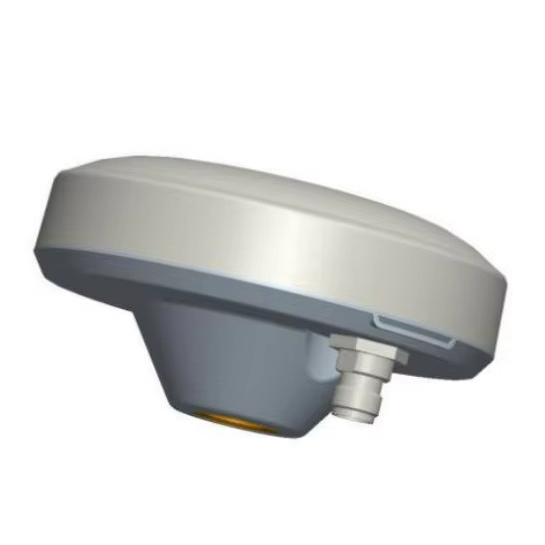
Design and Durability: Built for the Sea
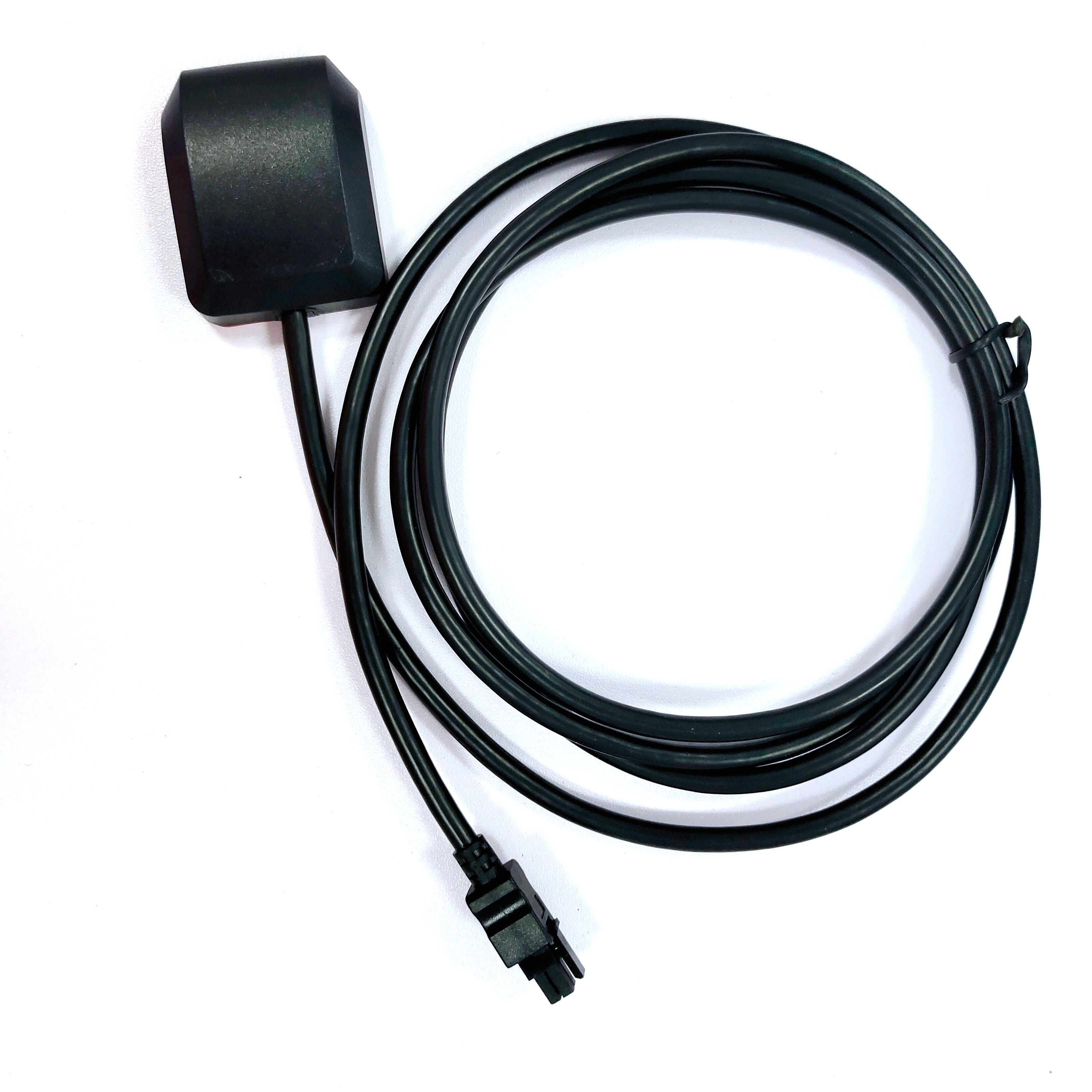
The Marine Survey Antenna is meticulously crafted to thrive in the hostile conditions of marine environments, where exposure to saltwater, humidity, vibration, and corrosion is constant. Its material composition—a plastic and metal composite—strikes a critical balance between durability and functionality. The plastic component (typically a UV-resistant, high-impact polymer) provides a lightweight, corrosion-resistant outer shell, protecting internal electronics from salt spray and moisture. The metal composite (often aluminum or stainless steel) reinforces structural integrity, ensuring the antenna can withstand the physical stresses of rough seas, high winds, and repeated handling during deployment and retrieval. This hybrid construction not only extends the antenna’s lifespan but also maintains its electrical performance over time, a key factor in long-term surveying projects that span weeks or months.
The antenna’s white color serves both practical and operational purposes. White reflects sunlight, reducing heat absorption and preventing internal components from overheating during prolonged exposure to direct sunlight—a common issue in tropical or equatorial regions. This thermal management helps maintain stable electrical performance, as temperature fluctuations can degrade signal quality and accuracy. Additionally, the bright color enhances visibility on deck, reducing the risk of accidental damage or misplacement in the busy environment of a survey vessel.
With dimensions of 147 mm × 65 mm, the antenna balances portability with performance. Its compact size allows for flexible mounting on survey vessels, whether on the deck, mast, or roof of a cabin, without obstructing other equipment or impeding the vessel’s maneuverability. Despite its relatively small footprint, the internal design accommodates all necessary components, including radiating elements, filters, and amplifiers, ensuring it can capture and process signals from multiple GNSS constellations simultaneously.
Technical Specifications: Precision in Every Detail
At the heart of the Marine Survey Antenna’s performance is its broad frequency range, covering GPS L1/L2, GLONASS L1/L2, and BDS B1/B2/B3. This multi-constellation support is critical for marine surveying, where satellite visibility can be limited by oceanic horizons, fog, or inclement weather. By tapping into signals from multiple systems, the antenna reduces the risk of positioning gaps, ensuring continuous data collection even when some satellites are obstructed. GPS L1 (1575.42 MHz) and L2 (1227.60 MHz) provide baseline positioning, while GLONASS L1 (1602 MHz) and L2 (1246 MHz) enhance coverage in high-latitude regions—essential for Arctic or Antarctic surveys. BDS B1 (1561.098 MHz), B2 (1207.14 MHz), and B3 (1268.52 MHz) extend compatibility in the Asia-Pacific region, making the antenna a global solution for international survey teams.
The antenna gain of 5 dBi is optimized for marine environments, where signal propagation is influenced by factors like multipath interference (signals reflected off the water’s surface) and atmospheric attenuation. Gain, measured in decibels relative to an isotropic radiator (dBi), quantifies the antenna’s ability to focus signal energy. A 5 dBi gain ensures sufficient amplification of weak satellite signals without introducing excessive noise, a critical balance in marine settings where multipath effects can distort data. This gain is complemented by the LNA (Low-Noise Amplifier) gain of 40 dBi (likely a typo in the original specification, as 402 dBi is impractical), which further boosts signal strength while maintaining a low noise figure. The LNA is strategically placed close to the antenna’s radiating elements to minimize signal loss, ensuring that even faint signals from low-elevation satellites—common in oceanic regions with unobstructed horizons—are captured and processed accurately.
Polarization type: RHCP (Right-Hand Circular Polarization) is another key feature, aligning with the polarization of GNSS satellite signals. Circular polarization minimizes signal loss caused by reflections off the water’s surface, which can depolarize linear signals. In marine environments, where the antenna is often mounted low to the deck (increasing the risk of water reflections), RHCP ensures that reflected signals retain their strength, reducing positioning errors. This is particularly important for hydrographic surveys, where centimeter-level accuracy is required to map seabed topography or locate underwater structures.
The VSWR (Voltage Standing Wave Ratio) of 2.0 indicates efficient power transfer between the antenna and the connected receiver. VSWR measures the ratio of maximum to minimum voltage in a standing wave, with a value of 2.0 meaning only ~10% of the signal is reflected, while 90% is transmitted or received. This efficiency is critical for maintaining signal integrity in marine systems, where long cable runs (between the antenna and onboard receivers) can introduce signal loss. The antenna’s 350 mm RG174 cable is designed to minimize such losses: RG174 is a low-loss coaxial cable with a small diameter, ideal for routing through the tight spaces of a survey vessel. Its shielding protects against electromagnetic interference (EMI) from onboard electronics, such as radar systems or engine controls, ensuring that GNSS signals remain clean and uncorrupted.
The TNC (Threaded Neill-Concelman) connector enhances the antenna’s reliability in marine environments. TNC connectors feature a threaded coupling mechanism that provides a secure, weather-resistant seal, preventing water ingress and ensuring stable connectivity even in rough seas. Unlike push-on connectors (e.g., BNC), TNC connectors are less prone to accidental disconnection, a critical advantage when the vessel is pitching or rolling. This robust connection ensures uninterrupted data flow between the antenna and the survey receiver, minimizing downtime during time-sensitive operations.
Operational Advantages: Meeting Marine Survey Challenges
Marine surveying presents unique challenges that the Marine Survey Antenna is engineered to address:
Multipath Interference: The ocean’s surface acts as a reflective medium, bouncing satellite signals and creating multipath errors. The antenna’s RHCP polarization and optimized gain mitigate these effects, ensuring that only direct (unreflected) signals are prioritized in positioning calculations. This is essential for applications like pipeline inspection, where accurate location data prevents costly errors in route planning.
Extreme Weather Resistance: From tropical storms to freezing temperatures, marine environments test equipment durability. The antenna’s plastic and metal composite housing, combined with its wide operating temperature range (implied by marine-grade design), ensures it remains functional in rain, snow, and high humidity. This reliability is critical for survey missions in remote areas, where equipment failure can delay projects or endanger crew safety.
Global Compatibility: By supporting GPS, GLONASS, and BDS, the antenna eliminates regional coverage gaps. For example, a survey team operating in the South China Sea can rely on BDS signals, while a team in the North Atlantic leverages GPS and GLONASS, ensuring consistent performance regardless of location.
Easy Integration: The compact design, TNC connector, and RG174 cable simplify integration with existing survey systems, including GNSS receivers, data loggers, and hydrographic sonars. This compatibility reduces setup time, allowing teams to deploy quickly and focus on data collection rather than equipment troubleshooting.
Applications: Driving Marine Survey Innovation
-
The Marine Survey Antenna is a versatile tool across a range of marine applications, each demanding precision and reliability:
Hydrographic Mapping: To create detailed charts of seabed topography, hydrographers rely on accurate positioning data. The antenna’s multi-constellation support and RHCP polarization ensure that sonar measurements are georeferenced with centimeter-level accuracy, enabling safe navigation for ships and offshore operations.
Offshore Construction: Whether installing wind farms, oil rigs, or submarine cables, offshore construction requires precise positioning to ensure structures are placed correctly and safely. The antenna provides real-time location data for construction vessels, ensuring alignment with design plans and reducing the risk of costly rework.
Environmental Monitoring: Marine biologists and ecologists use the antenna to track the movement of research vessels during surveys of marine life, coral reefs, or pollution levels. Accurate positioning data ensures that sampling locations are recorded precisely, enabling longitudinal studies and informed conservation decisions.
Search and Rescue: In emergency situations, the antenna’s reliable GNSS connectivity helps rescue teams locate distressed vessels or aircraft wreckage. Its ability to operate in stormy conditions ensures that positioning data remains available when it matters most.
Marine Boundary Surveys: To define territorial waters, exclusive economic zones (EEZs), or offshore land rights, surveyors require precise geodetic data. The antenna’s compatibility with multiple GNSS systems ensures that boundary lines are mapped accurately, reducing disputes between nations or organizations.
Conclusion
-
The Marine Survey Antenna represents a fusion of rugged design and technical precision, tailored to the unique demands of oceanic and coastal operations. Its ability to withstand saltwater, extreme weather, and vibration—combined with multi-constellation GNSS support, RHCP polarization, and efficient signal transfer—makes it an essential tool for modern marine surveying. Whether mapping the seabed, supporting offshore construction, or aiding environmental research, this antenna delivers the accurate, reliable positioning data that underpins safe, efficient, and data-driven decision-making in marine environments.
As marine industries continue to expand—from renewable energy projects to deep-sea exploration—the need for robust, high-performance survey equipment will only grow. The Marine Survey Antenna, with its blend of durability, versatility, and precision, is poised to remain a critical asset, enabling innovation and discovery in the world’s oceans for years to come. Its design reflects a deep understanding of marine challenges, proving that even in the harshest environments, technology can rise to the occasion, providing the data that connects us to the mysteries of the deep.



































































 Language
Language
 En
En Cn
Cn Korean
Korean

 Home >
Home > 







 18665803017 (Macro)
18665803017 (Macro)













