GNSS, encompassing constellations like GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou, relies on satellites transmitting signals that carry information about their position and time. However, factors such as atmospheric conditions, signal blockage from buildings or natural obstacles, and interference from other electronic devices can significantly weaken these signals. High sensitivity embedded GNSS antennas are crucial for applications where uninterrupted and accurate positioning is non - negotiable.
Embedded within various devices, these antennas offer the advantage of space - efficient integration, making them ideal for compact electronics such as smartphones, wearable devices, IoT sensors, and asset trackers. By enhancing the signal - receiving capabilities, they ensure that these devices can provide reliable location - based services, from navigation and tracking to emergency response and environmental monitoring. As the demand for precise positioning in challenging environments continues to grow, high sensitivity embedded GNSS antennas are set to play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of location - aware technologies.
Design and Construction
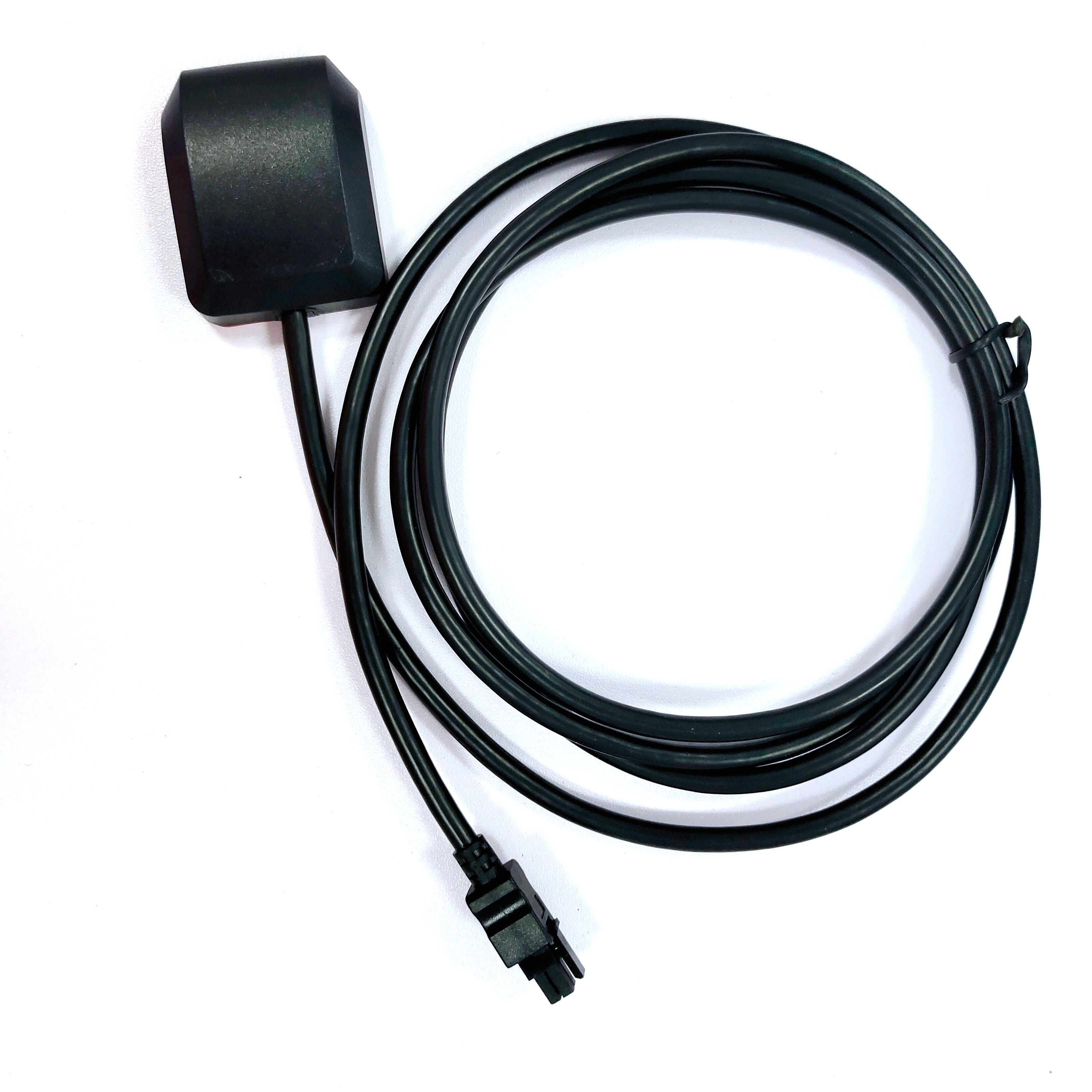
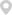
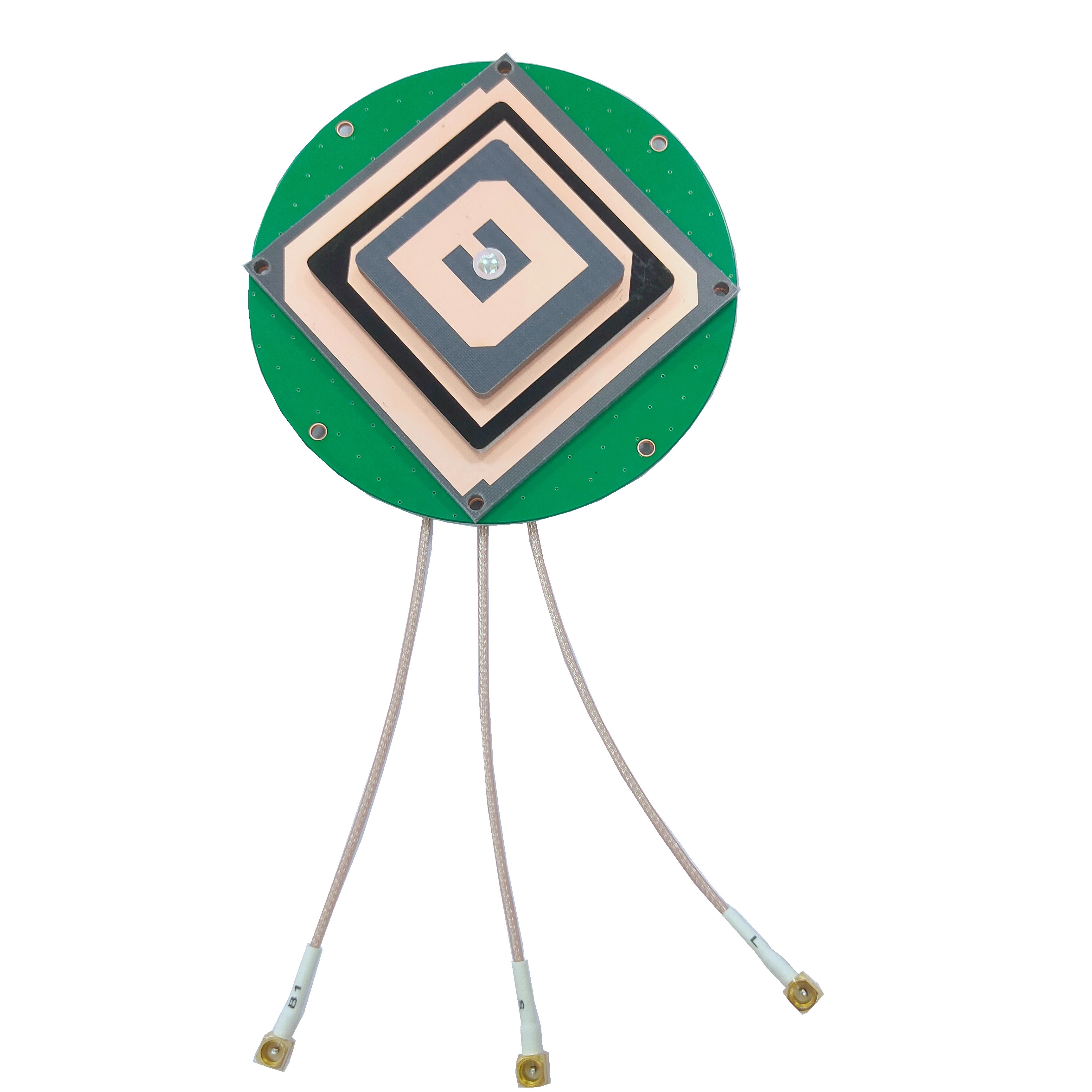
The design and construction of high sensitivity embedded GNSS antennas prioritize signal reception enhancement while maintaining a compact form factor suitable for integration. The antenna element, often based on microstrip or patch designs, is optimized for maximum sensitivity. Advanced electromagnetic simulation tools are employed to fine - tune the shape, size, and configuration of the metallic patch, which is typically made of copper or gold. These simulations help engineers achieve better impedance matching and radiation patterns, enabling the antenna to capture weak signals more effectively.
Materials selection is critical in the construction process. Dielectric substrates with low loss tangents and high dielectric constants are preferred to reduce signal losses and increase the antenna's efficiency. Ceramic - based substrates are commonly used due to their excellent electrical and thermal properties, which contribute to stable performance across a wide range of frequencies and environmental conditions.
To further boost sensitivity, high - performance low - noise amplifiers (LNAs) are integrated into the antenna design. These LNAs amplify the weak incoming signals while minimizing the addition of noise, ensuring that the signals transmitted to the GNSS receiver are as clean and strong as possible. Additionally, advanced filtering techniques are incorporated to reject unwanted frequencies and interference, allowing only the relevant GNSS signals to pass through. The overall packaging of the antenna is designed to protect the internal components from environmental factors and electromagnetic interference, ensuring reliable operation in diverse conditions.
The design and construction of high sensitivity embedded GNSS antennas prioritize signal reception enhancement while maintaining a compact form factor suitable for integration. The antenna element, often based on microstrip or patch designs, is optimized for maximum sensitivity. Advanced electromagnetic simulation tools are employed to fine - tune the shape, size, and configuration of the metallic patch, which is typically made of copper or gold. These simulations help engineers achieve better impedance matching and radiation patterns, enabling the antenna to capture weak signals more effectively.
Materials selection is critical in the construction process. Dielectric substrates with low loss tangents and high dielectric constants are preferred to reduce signal losses and increase the antenna's efficiency. Ceramic - based substrates are commonly used due to their excellent electrical and thermal properties, which contribute to stable performance across a wide range of frequencies and environmental conditions.
To further boost sensitivity, high - performance low - noise amplifiers (LNAs) are integrated into the antenna design. These LNAs amplify the weak incoming signals while minimizing the addition of noise, ensuring that the signals transmitted to the GNSS receiver are as clean and strong as possible. Additionally, advanced filtering techniques are incorporated to reject unwanted frequencies and interference, allowing only the relevant GNSS signals to pass through. The overall packaging of the antenna is designed to protect the internal components from environmental factors and electromagnetic interference, ensuring reliable operation in diverse conditions.
The operation of high sensitivity embedded GNSS antennas is centered around efficient signal reception, amplification, and processing. When weak GNSS signals reach the antenna element, they induce electrical currents due to resonance at the appropriate frequencies. These initial signals are extremely faint and require immediate amplification to be useful for further processing.
The integrated low - noise amplifier (LNA) plays a pivotal role in this stage, boosting the signal strength while keeping the noise level to a minimum. After amplification, the signals pass through a series of filters. Band - pass filters are used to isolate the frequencies within the GNSS bands, rejecting unwanted frequencies from other radio - frequency sources. Notch filters may also be utilized to specifically target and suppress frequencies that are known to cause interference.
Once the signals are amplified and filtered, they are transmitted to the GNSS receiver. The receiver then uses these processed signals, along with information about the satellite positions and time stamps, to calculate the precise location of the device through trilateration or multilateration. High sensitivity embedded GNSS antennas ensure that even in challenging signal environments, enough signal strength and quality are maintained for the receiver to perform accurate positioning calculations.
-
High sensitivity embedded GNSS antennas offer significant advantages, chief among them being their ability to provide accurate positioning in difficult signal environments. This is invaluable for applications in urban areas, where tall buildings can block or weaken GNSS signals, and in indoor - outdoor transition scenarios. The enhanced sensitivity also improves the reliability of location - based services, reducing the chances of signal dropouts or inaccurate positioning.
Their compact and embedded nature allows for seamless integration into a wide range of devices, enabling the development of smaller, more lightweight electronics without sacrificing positioning capabilities. This is particularly beneficial for wearable devices and IoT sensors, where space and power consumption are at a premium.
However, these antennas also face several challenges. One of the main hurdles is achieving a balance between sensitivity and power consumption. High - performance components used to boost sensitivity, such as advanced LNAs, often consume more power, which can be a concern for battery - powered devices. Additionally, the design complexity and the use of specialized components can increase the manufacturing cost, potentially limiting their widespread adoption. Another challenge is electromagnetic interference (EMI), as these sensitive antennas can be easily affected by nearby electronic devices, requiring robust shielding and filtering solutions.
-
High sensitivity embedded GNSS antennas find extensive applications across multiple sectors. In the consumer electronics industry, they enable more accurate navigation and location - based features in smartphones and wearable devices, enhancing user experiences. In the IoT domain, these antennas are crucial for asset tracking devices, allowing for precise monitoring of valuable assets in various environments. They also play a vital role in environmental monitoring, where sensors equipped with high sensitivity antennas can provide accurate location - tagged data, even in remote or hard - to - reach areas.
Looking ahead, future trends for high sensitivity embedded GNSS antennas include further miniaturization without sacrificing performance. This will be driven by advancements in materials science and manufacturing techniques, such as nanotechnology. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms is also on the horizon. These technologies can be used to optimize the antenna's performance in real - time, adapt to changing signal environments, and further enhance sensitivity. Additionally, as 5G and other advanced communication technologies become more prevalent, there will be a need for seamless integration of GNSS antennas to enable more accurate and reliable location - based services.
Conclusion
High sensitivity embedded GNSS antennas are indispensable for achieving accurate positioning in challenging environments. Their ability to capture weak signals and provide reliable location - based services has made them essential components in a wide range of devices. While they face challenges related to power consumption, cost, and interference, ongoing technological advancements offer promising solutions. As the demand for precise positioning continues to grow across various industries, high sensitivity embedded GNSS antennas will remain at the forefront of innovation, driving the development of more advanced and reliable location - aware technologies.



































































 Language
Language
 En
En Cn
Cn Korean
Korean

 Home >
Home > 







 18665803017 (Macro)
18665803017 (Macro)













