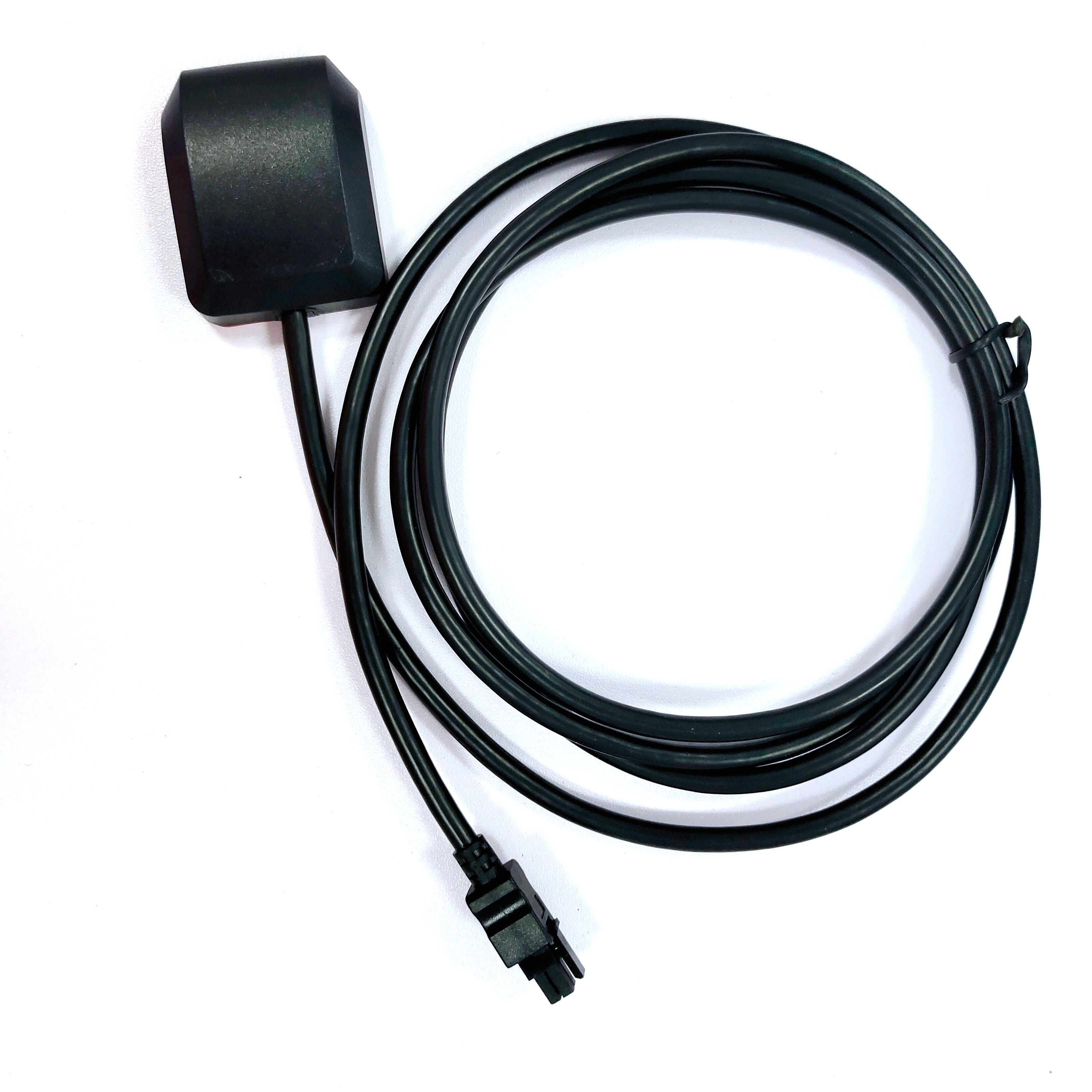
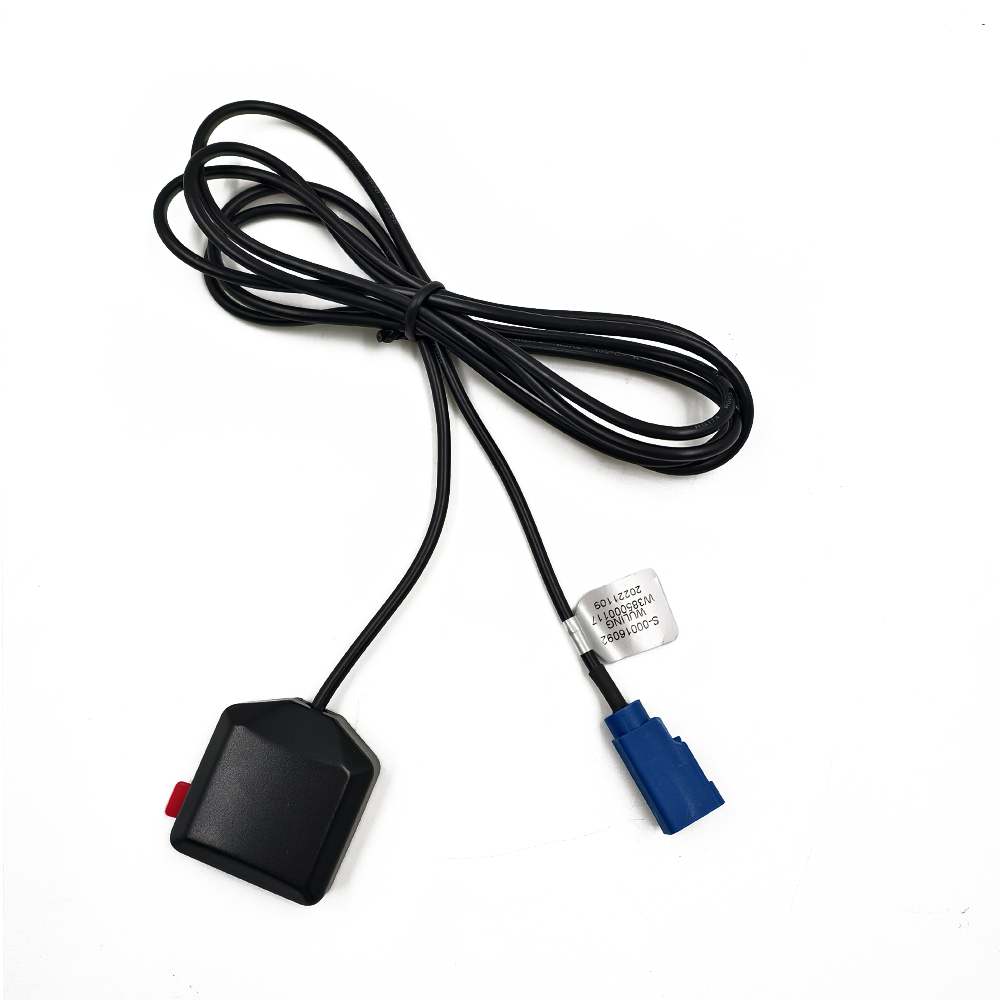
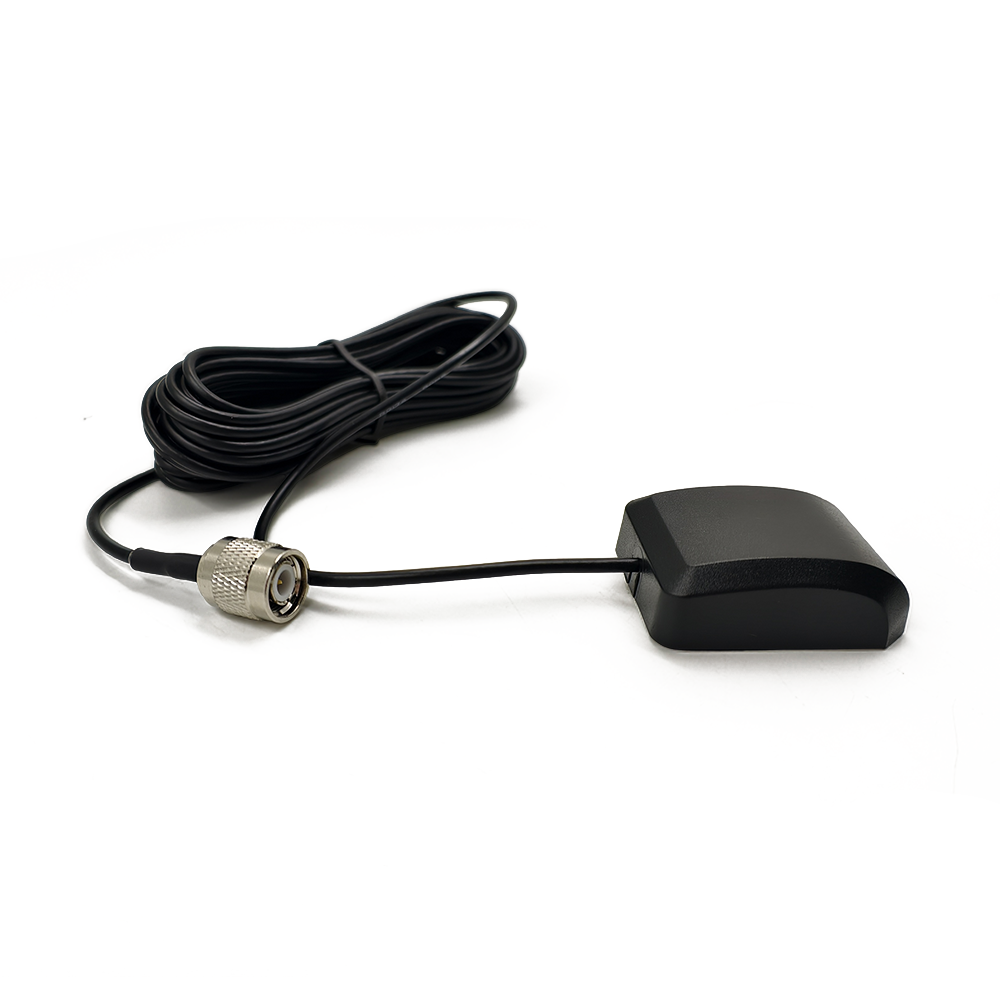
Connectivity: TNC
The GPS BD Antenna features a TNC (Threaded Neill-Concelman) connector, which is a robust and reliable choice for RF (radio frequency) applications. TNC connectors are known for their excellent mechanical durability and superior electrical performance, making them ideal for use in harsh environments. The TNC connector on the GPS BD Antenna ensures a secure and stable connection, minimizing the risk of signal loss or interference.
TNC connectors are commonly used in various industries, including telecommunications, military, and aerospace, due to their ability to handle high frequencies and provide excellent shielding against electromagnetic interference (EMI). The threaded design of the TNC connector allows for easy installation and removal, while the gold-plated contacts ensure low insertion loss and high reliability.
In the context of the GPS BD Antenna, the TNC connector plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the RF signal. The connector's design helps to minimize signal degradation, ensuring that the antenna can effectively receive and transmit signals from the GPS and BeiDou satellite systems. This is particularly important in applications where precise positioning and timing are critical, such as in automotive navigation systems and IoT devices.
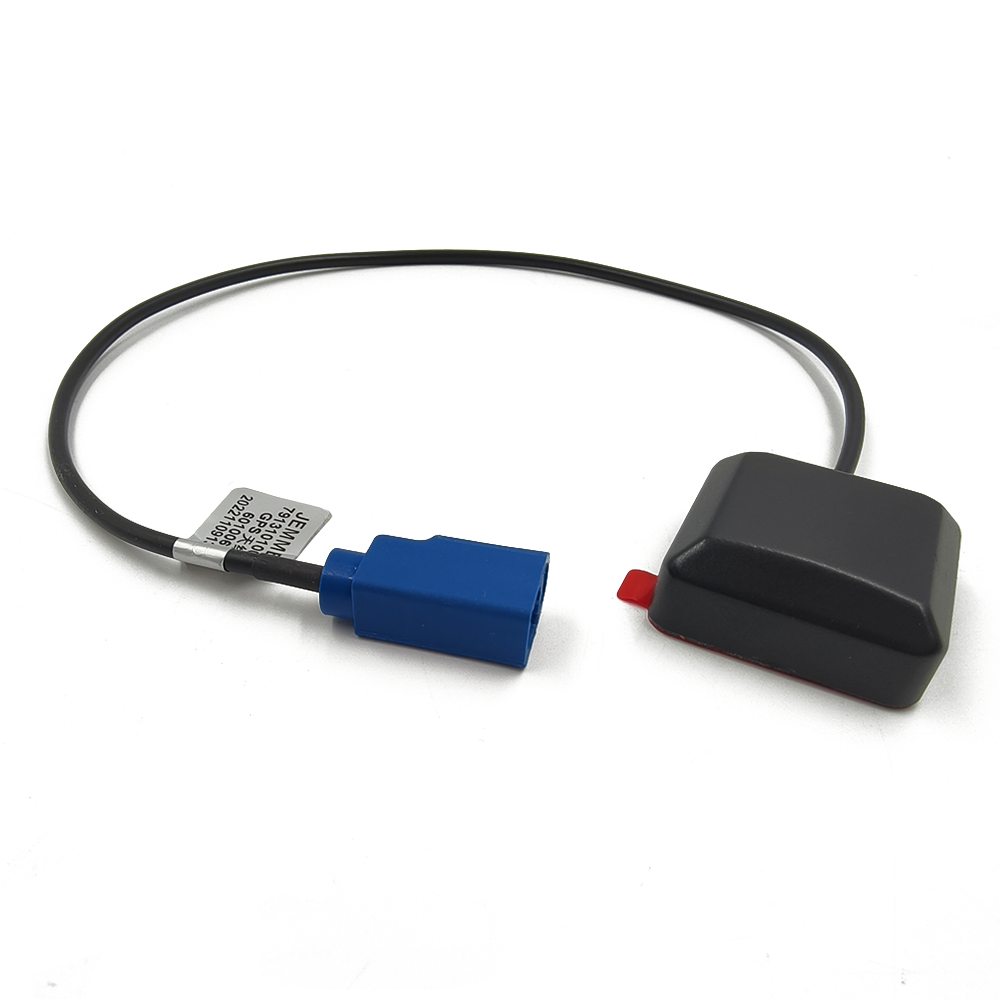
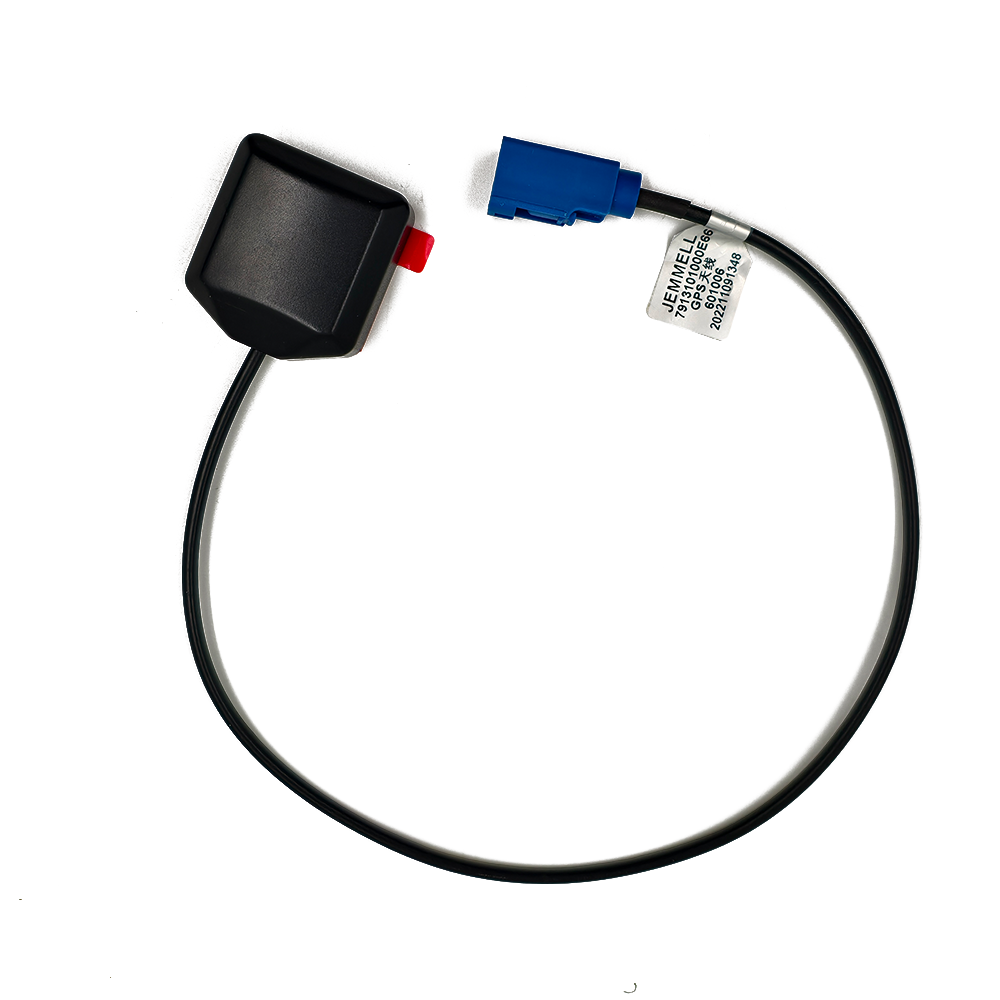
Material: ABS
The GPS BD Antenna is constructed using ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) plastic, a versatile and durable material commonly used in the manufacturing of electronic components. ABS is known for its excellent mechanical properties, including high impact resistance, toughness, and rigidity. These characteristics make it an ideal choice for the housing of the GPS BD Antenna, as it can withstand the rigors of various environmental conditions.
ABS plastic is also lightweight, which is an important consideration for applications where weight is a factor, such as in automotive and portable IoT devices. The material's ability to be easily molded and shaped allows for the creation of complex and intricate designs, enabling the GPS BD Antenna to be compact and efficient.
In addition to its mechanical properties, ABS plastic offers good thermal stability, which is essential for the proper functioning of the antenna across a wide range of temperatures. The material's resistance to chemicals and UV radiation further enhances its suitability for outdoor and industrial applications.
Polarity: ROHS
The term "polarity" in the context of the GPS BD Antenna refers to its compliance with the RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) directive. RoHS is a European Union regulation that restricts the use of certain hazardous materials in electronic and electrical equipment. The directive aims to reduce the environmental impact of electronic waste and protect human health by limiting the use of substances such as lead, mercury, cadmium, and hexavalent chromium.
The GPS BD Antenna's compliance with RoHS indicates that it has been manufactured using environmentally friendly materials and processes. This not only ensures that the antenna is safe for use but also contributes to the overall sustainability of the product. RoHS compliance is becoming increasingly important in the global market, as more countries adopt similar regulations to protect the environment and public health.
For manufacturers and consumers, RoHS compliance is a key factor in the selection of electronic components. It demonstrates a commitment to responsible manufacturing practices and helps to ensure that products meet the highest standards of quality and safety. In the case of the GPS BD Antenna, RoHS compliance is an important aspect of its design, reflecting the manufacturer's dedication to producing high-quality, environmentally friendly products.
Impedance: 50 Ohms
The GPS BD Antenna has an impedance of 50 ohms, which is a standard value for RF antennas and transmission lines. Impedance matching is a critical aspect of RF design, as it ensures that the maximum amount of power is transferred from the source to the load, minimizing signal reflection and loss.
A 50-ohm impedance is widely used in RF systems because it provides a good balance between power handling capability and signal integrity. It is compatible with a wide range of RF components and devices, making it a versatile choice for various applications. The 50-ohm impedance of the GPS BD Antenna ensures that it can be easily integrated into existing RF systems, providing optimal performance and reliability.
Impedance matching is particularly important in GPS and BeiDou systems, where accurate signal reception is essential for precise positioning and timing. Any mismatch in impedance can result in signal reflections, which can cause interference and reduce the overall performance of the system. By maintaining a consistent 50-ohm impedance, the GPS BD Antenna helps to ensure that the RF signals are transmitted and received efficiently, without significant loss or distortion.
Frequency Range: 1.57542 GHz & 1.561 GHz
The GPS BD Antenna is designed to operate within the frequency range of 1.57542 GHz and 1.561 GHz, which corresponds to the L1 frequency band used by the GPS and BeiDou satellite systems. The L1 frequency band is a fundamental component of these systems, as it is used to transmit the primary navigation signals that enable precise positioning, navigation, and timing.
The GPS system operates at a frequency of 1.57542 GHz, while the BeiDou system uses a frequency of 1.561 GHz. By covering both of these frequencies, the GPS BD Antenna provides dual-system compatibility, allowing it to receive signals from both GPS and BeiDou satellites simultaneously. This dual-system capability enhances the accuracy and reliability of the positioning information, as it increases the number of available satellites and improves the overall signal quality.
The ability to operate within this specific frequency range is crucial for the proper functioning of the GPS BD Antenna. It ensures that the antenna can effectively capture and process the signals transmitted by the GPS and BeiDou satellites, providing accurate and reliable positioning data for various applications.
VSWR: ≤ 2.0
The Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR) of the GPS BD Antenna is specified as ≤ 2.0, which indicates a good level of impedance matching and signal efficiency. VSWR is a measure of the efficiency of an antenna in transmitting and receiving RF signals. A VSWR value of 1.0 represents a perfect match, with no signal reflection or loss. In practical applications, a VSWR value of ≤ 2.0 is considered acceptable, as it indicates that the majority of the RF energy is being effectively transferred to and from the antenna.
A VSWR of ≤ 2.0 means that the GPS BD Antenna has a low level of signal reflection, which minimizes the risk of interference and reduces signal loss. This is particularly important in GPS and BeiDou systems, where accurate signal reception is essential for precise positioning and timing. By maintaining a VSWR of ≤ 2.0, the GPS BD Antenna ensures that it can effectively capture and process the signals transmitted by the satellites, providing reliable and accurate positioning data.
Peak Gain: 28 dBi
The peak gain of the GPS BD Antenna is specified as 28 dBi, which indicates its ability to effectively capture and amplify the RF signals transmitted by the GPS and BeiDou satellites. Gain is a measure of an antenna's ability to focus and direct the RF energy, and it is expressed in decibels (dB) relative to an isotropic radiator (dBi).
A peak gain of 28 dBi is a relatively high value for a GPS antenna, indicating that the antenna is capable of capturing weak signals and amplifying them to a usable level. This is particularly important in areas with poor satellite visibility, such as urban environments or dense foliage, where the signal strength may be reduced. The high gain of the GPS BD Antenna helps to ensure that it can effectively receive signals from multiple satellites, even in challenging conditions.
The high gain of the GPS BD Antenna also contributes to its overall performance and reliability. By amplifying the received signals, the antenna can provide more accurate and precise positioning data, which is essential for applications such as automotive navigation and IoT devices. The high gain also helps to reduce the risk of signal interference and loss, ensuring that the antenna can operate effectively in a wide range of environments.
Polarization: Linear
-
The GPS BD Antenna is designed with linear polarization, which refers to the orientation of the electric field vector of the RF signal. In linear polarization, the electric field vector oscillates in a single plane, either horizontally or vertically. This is in contrast to circular polarization, where the electric field vector rotates in a circular pattern.
Linear polarization is a common choice for GPS and BeiDou antennas, as it provides a good balance between signal strength and directional sensitivity. The linear polarization of the GPS BD Antenna ensures that it can effectively capture and process the signals transmitted by the satellites, which are also typically linearly polarized.
The choice of linear polarization is particularly important for applications where the antenna may be mounted in a fixed position, such as on a vehicle or a building. In these cases, the linear polarization helps to ensure that the antenna can maintain a consistent and stable signal, even if the orientation of the antenna changes. This is essential for accurate and reliable positioning, navigation, and timing.



































































 Language
Language
 En
En Cn
Cn Korean
Korean

 Home >
Home > 








 18665803017 (Macro)
18665803017 (Macro)













